nagiosでJavaプログラムの監視と再起動
nagiosについての全投稿は/tag/nagiosにあるので参照されたい。
ここではJavaプログラムを監視し、落ちている場合は警報を出すと共に再起動することを考える。対象としてはtomcatである。良く落ちることがあるのだ。tomcatの再起動は他にも方法があるようだ、何もnagiosにやらせる必要はない。
設定ファイルと動作
nagiosのインストールと全体的な動作はnagiosのインストールと最小限の設定で説明したが、ここでおさらいしておく。
設定ファイルは/etc/nagiosディレクトリにあり、
- nagios.cfgがnagiosの動作を設定するファイルだが、ここから他のファイルをインクルードされている。
- contacts.cfgでは異常発生時のメールアドレスを定義する
- localhost.cfgはローカルホスト監視用の定義が記述される。もちろん、外部ホストを監視したい場合は同様のファイルを作成して、nagios.cfgからインクルードさせる。
- commands.cfgはlocalhost.cfg等で使用するコマンドが定義される。ここから呼び出されるコマンドの多くがプラグインとして提供されており、nagiosとは別途インストールしなければならない。
設定ファイルを変更したら、設定チェックをしてから再起動する。
nagios -v /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg
service nagios restart
コマンド引数
localhost.cfgにはコマンドの呼び出し方を書き、command.cfgにはコマンドの定義を記述し、これらのコマンドはプラグインとなっている。そのコマンドの呼び出し方が問題になる。
引数はプラグインコマンドを–help付きで呼び出すことでわかる。
# /usr/lib64/nagios/plugins/check_http --help
check_http v2.2.1 (nagios-plugins 2.2.1)
Copyright (c) 1999 Ethan Galstad <nagios@nagios.org>
Copyright (c) 1999-2014 Nagios Plugin Development Team
<devel@nagios-plugins.org>
This plugin tests the HTTP service on the specified host. It can test
normal (http) and secure (https) servers, follow redirects, search for
strings and regular expressions, check connection times, and report on
certificate expiration times.
Usage:
check_http -H <vhost> | -I <IP-address> [-u <uri>] [-p <port>]
[-J <client certificate file>] [-K <private key>]
[-w <warn time>] [-c <critical time>] [-t <timeout>] [-L] [-E] [-a auth]
[-b proxy_auth] [-f <ok|warning|critcal|follow|sticky|stickyport>]
[-e <expect>] [-d string] [-s string] [-l] [-r <regex> | -R <case-insensitive regex>]
[-P string] [-m <min_pg_size>:<max_pg_size>] [-4|-6] [-N] [-M <age>]
[-A string] [-k string] [-S <version>] [--sni] [-C <warn_age>[,<crit_age>]]
[-T <content-type>] [-j method]
NOTE: One or both of -H and -I must be specified
Options:
-h, --help
Print detailed help screen
-V, --version
Print version information
--extra-opts=[section][@file]
Read options from an ini file. See
https://www.nagios-plugins.org/doc/extra-opts.html
for usage and examples.
-H, --hostname=ADDRESS
Host name argument for servers using host headers (virtual host)
Append a port to include it in the header (eg: example.com:5000)
-I, --IP-address=ADDRESS
IP address or name (use numeric address if possible to bypass DNS lookup).
-p, --port=INTEGER
Port number (default: 80)
-4, --use-ipv4
Use IPv4 connection
-6, --use-ipv6
Use IPv6 connection
-S, --ssl=VERSION[+]
Connect via SSL. Port defaults to 443. VERSION is optional, and prevents
auto-negotiation (2 = SSLv2, 3 = SSLv3, 1 = TLSv1, 1.1 = TLSv1.1,
1.2 = TLSv1.2). With a '+' suffix, newer versions are also accepted.
--sni
Enable SSL/TLS hostname extension support (SNI)
-C, --certificate=INTEGER[,INTEGER]
Minimum number of days a certificate has to be valid. Port defaults to 443
(when this option is used the URL is not checked.)
-J, --client-cert=FILE
Name of file that contains the client certificate (PEM format)
to be used in establishing the SSL session
-K, --private-key=FILE
Name of file containing the private key (PEM format)
matching the client certificate
-e, --expect=STRING
Comma-delimited list of strings, at least one of them is expected in
the first (status) line of the server response (default: HTTP/1.)
If specified skips all other status line logic (ex: 3xx, 4xx, 5xx processing)
-d, --header-string=STRING
String to expect in the response headers
-s, --string=STRING
String to expect in the content
-u, --uri=PATH
URI to GET or POST (default: /)
--url=PATH
(deprecated) URL to GET or POST (default: /)
-P, --post=STRING
URL encoded http POST data
-j, --method=STRING (for example: HEAD, OPTIONS, TRACE, PUT, DELETE, CONNECT)
Set HTTP method.
-N, --no-body
Don't wait for document body: stop reading after headers.
(Note that this still does an HTTP GET or POST, not a HEAD.)
-M, --max-age=SECONDS
Warn if document is more than SECONDS old. the number can also be of
the form "10m" for minutes, "10h" for hours, or "10d" for days.
-T, --content-type=STRING
specify Content-Type header media type when POSTing
-l, --linespan
Allow regex to span newlines (must precede -r or -R)
-r, --regex, --ereg=STRING
Search page for regex STRING
-R, --eregi=STRING
Search page for case-insensitive regex STRING
--invert-regex
Return CRITICAL if found, OK if not
-a, --authorization=AUTH_PAIR
Username:password on sites with basic authentication
-b, --proxy-authorization=AUTH_PAIR
Username:password on proxy-servers with basic authentication
-A, --useragent=STRING
String to be sent in http header as "User Agent"
-k, --header=STRING
Any other tags to be sent in http header. Use multiple times for additional headers
-E, --extended-perfdata
Print additional performance data
-L, --link
Wrap output in HTML link (obsoleted by urlize)
-f, --onredirect=<ok|warning|critical|follow|sticky|stickyport>
How to handle redirected pages. sticky is like follow but stick to the
specified IP address. stickyport also ensures port stays the same.
-m, --pagesize=INTEGER<:INTEGER>
Minimum page size required (bytes) : Maximum page size required (bytes)
-w, --warning=DOUBLE
Response time to result in warning status (seconds)
-c, --critical=DOUBLE
Response time to result in critical status (seconds)
-t, --timeout=INTEGER:<timeout state>
Seconds before connection times out (default: 10)
Optional ":<timeout state>" can be a state integer (0,1,2,3) or a state STRING
-v, --verbose
Show details for command-line debugging (Nagios may truncate output)
Notes:
This plugin will attempt to open an HTTP connection with the host.
Successful connects return STATE_OK, refusals and timeouts return STATE_CRITICAL
other errors return STATE_UNKNOWN. Successful connects, but incorrect reponse
messages from the host result in STATE_WARNING return values. If you are
checking a virtual server that uses 'host headers' you must supply the FQDN
(fully qualified domain name) as the [host_name] argument.
You may also need to give a FQDN or IP address using -I (or --IP-Address).
This plugin can also check whether an SSL enabled web server is able to
serve content (optionally within a specified time) or whether the X509
certificate is still valid for the specified number of days.
Please note that this plugin does not check if the presented server
certificate matches the hostname of the server, or if the certificate
has a valid chain of trust to one of the locally installed CAs.
Examples:
CHECK CONTENT: check_http -w 5 -c 10 --ssl -H www.verisign.com
When the 'www.verisign.com' server returns its content within 5 seconds,
a STATE_OK will be returned. When the server returns its content but exceeds
the 5-second threshold, a STATE_WARNING will be returned. When an error occurs,
a STATE_CRITICAL will be returned.
CHECK CERTIFICATE: check_http -H www.verisign.com -C 14
When the certificate of 'www.verisign.com' is valid for more than 14 days,
a STATE_OK is returned. When the certificate is still valid, but for less than
14 days, a STATE_WARNING is returned. A STATE_CRITICAL will be returned when
the certificate is expired.
CHECK CERTIFICATE: check_http -H www.verisign.com -C 30,14
When the certificate of 'www.verisign.com' is valid for more than 30 days,
a STATE_OK is returned. When the certificate is still valid, but for less than
30 days, but more than 14 days, a STATE_WARNING is returned.
A STATE_CRITICAL will be returned when certificate expires in less than 14 days
CHECK SSL WEBSERVER CONTENT VIA PROXY USING HTTP 1.1 CONNECT:
check_http -I 192.168.100.35 -p 80 -u https://www.verisign.com/ -S -j CONNECT -H www.verisign.com
all these options are needed: -I <proxy> -p <proxy-port> -u <check-url> -S(sl) -j CONNECT -H <webserver>
a STATE_OK will be returned. When the server returns its content but exceeds
the 5-second threshold, a STATE_WARNING will be returned. When an error occurs,
a STATE_CRITICAL will be returned.
Send email to help@nagios-plugins.org if you have questions regarding use
of this software. To submit patches or suggest improvements, send email to
devel@nagios-plugins.org
tomcatのポートを監視する
apacheもtomcatも監視するために、commands.cfgを変更する。
# 'check_http' command definition
define command{
command_name check_http
command_line $USER1$/check_http -I $HOSTADDRESS$ $ARG1$
}
となっているのだが、そもそもなぜ使われてもいない$ARG1$があるのか不明だが、これを以下に修正
# 'check_http' command definition
define command{
command_name check_http
command_line $USER1$/check_http -I $HOSTADDRESS$ -p $ARG1$
}
localhost.cfgのもともとのHTTPを変更し、TOMCATを加える。
define service{
use local-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name localhost
service_description HTTP
check_command check_http!80
notifications_enabled 1
}
define service{
use local-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name localhost
service_description TOMCAT
check_command check_http!8080
notifications_enabled 1
}
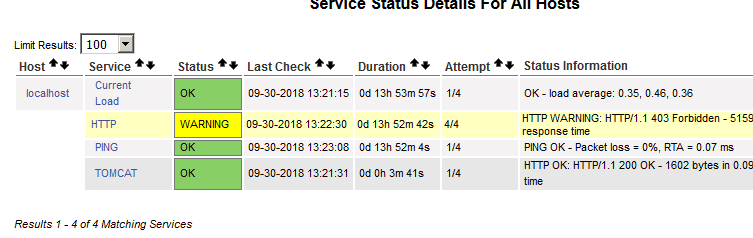
nagiosを再起動してしばらく経過すると、以下の表示になる。
イベントハンドラ
さて、サービスが落ちてしまった場合に、そのサービスを復旧させるための仕組みとしてイベントハンドラがある。もともとは、何らかの状態変更が起こった場合に走らせるものらしい。
イベントハンドラに説明がある。
以下のような具合だ。
localhost.cfgに以下を加える。
define service{
use local-service ; Name of service template to use
host_name localhost
service_description TOMCAT
check_command check_http!8080
notifications_enabled 1
event_handler restart_tomcat
}
comands.cfgに以下を加える
define command{
command_name restart_tomcat
command_line /foo/bar/nagios-restart-tomcat $SERVICESTATE$ $STATETYPE$ $SERVICEATTEMPT$
}
/foo/bar/nagios-restart-tomcatというシェルスクリプトを書く
#!/bin/sh
case "$1" in
CRITICAL)
case "$2" in
HARD)
# tomcatをリスタート
;;
esac
;;
esac
exit 0





ディスカッション
コメント一覧
まだ、コメントがありません